
Core Nutritionals Daily Health Pack
Product Description
We understand that being consistent with taking all your supplements can be tough, especially when your lifestyle is busy and schedule is full. At Core Nutritional’s®, we recognize this and put together a convenient daily packet that has everything you need to support your Crush It® lifestyle inside and outside of the gym. We’ve packed a combination of micronutrients, omega-3, probiotics, greens and reds, and products to support vital joints and organs, that can be highly beneficial to their overall function. Overall, a convenient daily pack of these supplements can help individuals maintain their health, support key body functions, and optimize well-being, even during a hectic and unpredictable lifestyle.
Ingredient Breakdown
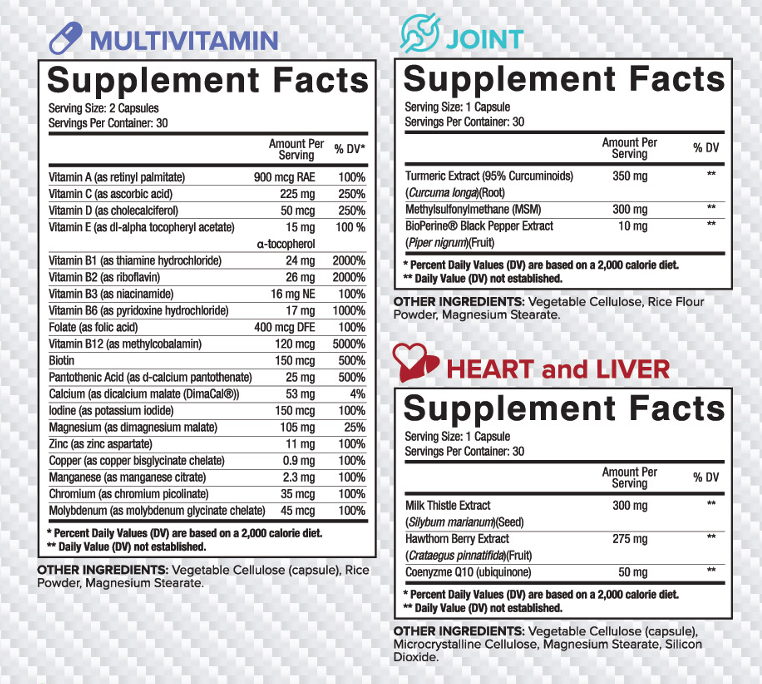
B Vitamins (Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, B6 [Pyridoxine], Folic Acid, B12, Biotin, and Pantothenic acid)
B vitamins are a group of eight essential vitamins with several critical functions in the body. Though both molecularly and physiologically distinct, they are also deeply interrelated in their effects, synthesis, and metabolism. Among the B-complex’s many critical roles are energy (protein, carbohydrates, and fat) metabolism, supporting and maintaining the healthy function of the adrenal glands, skeletal muscle function, and digestion.
While rates of metabolism and clearance differ between each B vitamin, all B vitamins are water-soluble and are thus not stored in fat. As a result, the body simply excretes excess B vitamins in the urine and requires replenishment (from food or supplements) to maintain the cell functions to which B vitamins contribute.
Vitamin A (as retinyl palmitate)
Beta carotene is itself not an essential vitamin but is rather the precursor to the fat-soluble and essential vitamin, vitamin A (Retinol). Like B vitamins, the term vitamin A refers to the compound class retinoids, comprised of retinol, retinal (also called retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and provitamin A compounds such as beta carotene.
As their names suggest, retinoids are critical to the function of human eyes and therefore to the maintenance of circadian rhythms (our “biological clock”). Vitamin A combines with proteins in the eye to form light-sensing cells that both facilitate vision and regulate our sleep-wake cycles.
Beyond its role in sight, vitamin A is also essential for cellular growth and differentiation and the immune system.
Vitamin C (as Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C is perhaps historically best-known for the treatment and prevention of scurvy, though it has many other roles in the body. For example, vitamin C catalyzes or is a cofactor in eight enzymatic reactions involved in the synthesis of collagen, the nutrient carnitine, and several neurotransmitters necessary for the proper function of the brain.
In the contemporary context, vitamin C is best known as a potent antioxidant. In addition to its intrinsic activity as an antioxidant, vitamin C has been shown in in vitro trials to regenerate alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E). As an antioxidant, vitamin C combats the detrimental effects of a group of compounds called radical oxygen species that, when produced, degrade the lipid membrane of the cell, and may cause internal damage. By “scavenging” these free radicals, vitamin C and other antioxidants form a defense against excess cellular damage.
Vitamin D3 (as Cholecalciferol)
Vitamin D, in its various forms, is not an essential nutrient – as it is produced endogenously within the body, as a reaction to the skin’s exposure to the sun – and thus not commonly considered a vitamin. Despite its technical classification, vitamin D (a hormone), is nevertheless an import and biologically-active compound, necessary for the calcium homeostasis and metabolism, along with increasing the absorption of magnesium and phosphate.
Vitamin E (as dl-alpha tocopherol acetate)
Vitamin E is another technical misnomer, as the term refers to a group of compounds known as tocopherols with eight biologically-active constituents: alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-tocopherol and alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-tocotrienol. Alpha-tocopherol is the principal bioactive in humans, though the presence of other tocopherols has been linked to beneficial effects.
As a result of its robust antioxidant activity, vitamin E assists in the maintenance and support of several physiological processes, though most notably sight and the immune system. Emerging research also suggests that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E inhibits an enzyme known as protein kinase C, and therefore contributes to the healthy regulation of smooth muscle cell growth and differentiation.
Calcium (as dicalcium malate (DimaCal®)
While best-known as the main bioactive in milk, and a compound that contributes to strong bones, calcium has numerous physiological effects in the body – including mediating vascular contraction and vasodilatation, muscle function, nerve transmission, intracellular signaling, and hormonal secretion. Homeostatic regulation of calcium, which the body cannot produce, requires sufficient levels of vitamin D.
When present in sufficient amounts, calcium is necessary for the adequate formation, function, and remodeling of both bone and teeth. Insufficient levels of calcium are associated with degenerative bone and joint disorders such as osteoporosis, wherein bone accretion slows or stops; thereby reducing bone mass and density and decreasing bone strength.
Iodine (as potassium iodide)
Iodine is a trace element naturally present in certain foods, including kelp. Iodine is a critical component for fetal development, especially during early pregnancy, as maternal T4 (thyroxine) is the sole source of fetal thyroid hormone. After birth, especially if breast-feeding, iodine remains an important constituent of a balanced-diet to maintain adequate T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) levels in the mother and for the proper cognitive development in the child.
As implied, however, the most important of iodine’s functions is assisting the body to produce and maintain healthy levels of both thyroid hormones and TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone, released by the pituitary). The thyroid hormones, in turn, regulate several critical biochemical reactions, including protein synthesis, and, along with norepinephrine/epinephrine, largely determine the body’s metabolic rate.
Magnesium (as Di-Magnesium Malate)
It is difficult to overstate the biological necessity of magnesium. Magnesium is a co-factor in over 300 enzymatic reactions that regulate essential physiological functions such as protein synthesis, glucose homeostasis, muscle and nerve function, and the maintenance and support of healthy blood pressure levels.
Magnesium is also required for the use of the body’s energy currency, ATP. To become biologically active, ATP must be bound to magnesium to form Mg-ATP. In addition, magnesium is necessary for the proper function of cells with calcium and potassium gated ion channels such as heart and muscle cells.
In men, magnesium (along with zinc) is necessary for the maintenance of healthy levels of testosterone.
Zinc (as Zinc Aspartate)
As an essential mineral, like magnesium, zinc is also involved in a wide-range of essential biological functions in the human body – and a requirement in the catalytic activity of over 100 enzymes.
Most notably, zinc is vital for immune function, protein synthesis, cellular division, and DNA synthesis. For immune function, zinc is required for the function of a group of immune cells known as neutrophils and macrophages, which eliminate pathological cells and their products from the body.
With magnesium, sufficient levels of zinc are also necessary for the production and maintenance of healthy levels of testosterone.
Copper (as Copper Bisglycinate Chelate)
Copper is a trace element necessary for the production, function, and maintenance of a diverse range of compounds involved in physiological function.
The brain, the heart, bone, and connective tissue specifically require copper or the enzymes it catalyzes to properly grow and differentiate their various cell types. Like many of the ingredients in Core MULTI, copper is also required for the homeostasis of other minerals, specifically zinc.
Manganese (as Manganese Citrate)
Manganese is a required element for not only humans, but all living organisms. Manganese primarily acts as an antioxidant, specifically scavenging a radical oxygen species known as superoxide.
Chromium (as Chromium Picolinate)
Chromium is an essential, though little understood, trace element found in certain foods and industrial compounds. Only one of chromium’s two forms, the form used in Core MULTI, chromium 3+, is biologically active.
While not as well-defined as other trace elements, chromium’s physiological actions nevertheless seem pivotal to the production and transmission of healthy levels of insulin. Emerging research also seems to suggest that chromium is directly involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Molybdenum (as Molybdenum Glycinate Chelate)
Molybdenum is an essential trace element, involved in at least four enzymatic reactions necessary for urea excretion and several other physiological functions.
GREENS
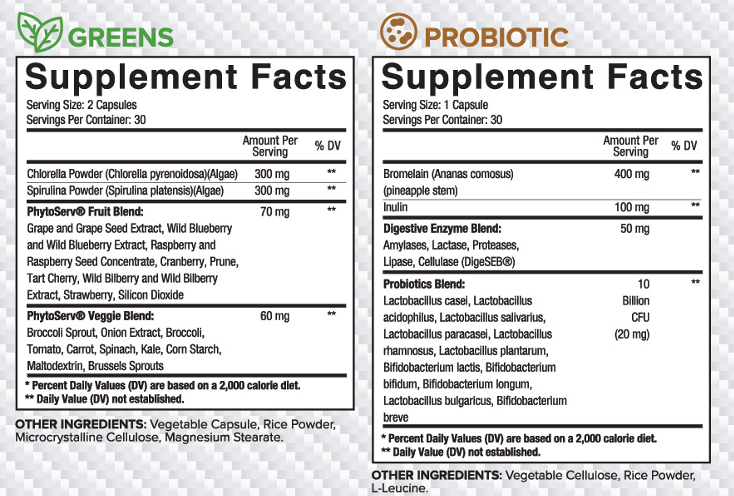
Chlorella and Spirulina Powder:
Chlorella and spirulina are the organisms behind the most common forms of green and blue/green algae, respectively. Chlorella has been variously classified as either a plant or a protist, while spirulina is a kind of cyanobacteria and thus classified as a bacterium. Regardless of the taxonomical differences between chlorella and spirulina, emerging evidence suggests that both have a range of benefits for human health.
The first benefit is that the macronutrient constituents in the plants themselves are favorable. Spirulina is a source of high-quality protein, γ-linolenic acid, and phycocyanin content. Chlorella, in turn, contains a variety of bioactives, including nucleic acids, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and β-glucans.
In addition to their macronutrient content, both chlorella and spirulina contain bioactive compounds that emerging evidence suggests have potential health effects. Polypeptide chains isolated from chlorella, for example, were shown in in vitro and animal models to be potent ACE inhibitors. ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of inactive Angiotensin I (AG-I) to the active Angiotensin II (AG-II). In turn, AG-II binds to the Angiotensin II receptor in smooth muscle and elicits the production of aldosterone – creating a hypertensive effect through direct and indirect means. While still preliminary, evidence suggests that the isolated polypeptides in chlorella may be ACE inhibitors.
Similar trials on the reduction of HbA1C, for example, demonstrate that these microalgae and their constituent parts may indeed be superfoods.
PhytoServ® Fruit Blend and Veggie Blend
PhytoServ® is a proprietary blend of plant-based extracts that condenses voluminous micronutrient sources into easy to deliver clinical doses that provide powerful antioxidant containing phytonutrients that can protect the body’s immune system from the harmful effects of oxidative stress. In the Fruit Blend you will receive a combination of:
- Grape Seed Extract
- Wild Blueberry Extract
- Raspberry Extract
- Cranberry
- Prune
- Tart Cherry
- Wild Bilberry Extract
- Strawberry
In the Veggie Blend you will receive:
- Broccoli Sprout
- Onion Extract
- Tomato
- Broccoli
- Carrot
- Spinach
- Kale
- Brussels Sprout
In the Core DAILY HEALTH PACK, we have included both the Fruit Blend and Veggie Blend so there are no gaps to your micronutrient protection.
BRAIN
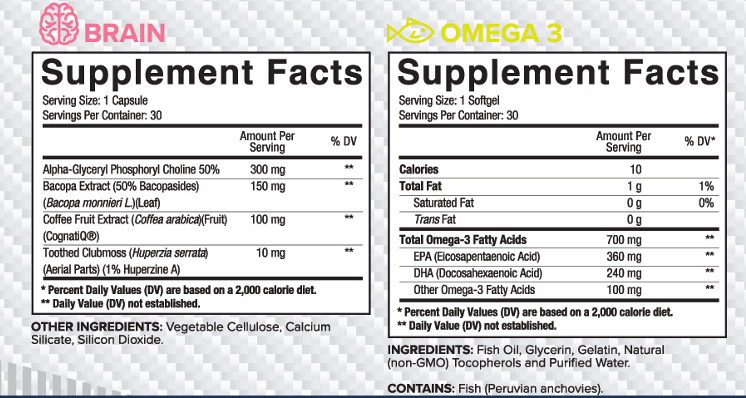
Alpha-GPC 50%
Of the known choline pro-drugs or precursors, Alpha GPC appears to have exert the greatest influence on circulating choline levels. Choline is an essential nutrient involved in numerous metabolic pathways, including DNA regulation and repair, protein function, and metabolism. Perhaps most importantly, the critical neurotransmitter acetylcholine is produced directly from free choline via cholinergic neurons. Acetylcholine is then responsible for several functions itself, most crucially as the compound which induces muscular contraction, and as the neuromodulator partially responsible for modulating risk/reward, arousal, and enhancing memory.
Choline’s essential role as a substrate for acetylcholine, and therefore brain development, is well documented in animal models. These studies demonstrate that levels of free maternal choline have a direct and fundamental impact on prenatal brain development, with the enhancements or deficits lasting into adulthood. Choline’s enhancing effect is particularly prominent in the hippocampus. In humans, the hippocampus is primarily involved in the consolidation of memory (taking short, episodic memory and translating it into long-term memory) and the learning of new information. Acetylcholine is a critical component in these processes, as mentioned above, and choline may therefore play a potential role in these processes as well by providing the substrate for acetylcholine synthesis.
Whether through these, or other independent mechanisms, a recent trial using Alpha GPC demonstrated a statistically significant increase to power output. In a placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial, 14 healthy volunteers, split into an Alpha GPC or placebo group, were tested on various exercises. In comparison to the placebo group, the Alpha GPC group experienced a 14% increase to bench press. The researchers hypothesize that the peak power increase was the result of a substantial acute increase to growth hormone, one of the observed effects of Alpha GPC supplementation.
Bacopa Extract (50% Bacopasides) (Bacopa monnieri L.) (Leaf)
Bacopa monnieri, also known as the water hyssop commonly, or as Brahmi in Ayurvedic texts, is a small creeping herb endemic to sub-tropical India. The herb has been used in traditional Indian medicine for well over one thousand years, with its first recorded usage coming in the 6th century A.D. In this traditional context, BM has been used for a wide-range of purposes, including as a treatment of asthma and epilepsy.
More recently, BM has been the subject of numerous cognition and memory trials, as the plant has a well-established nootropic effect. Likely through modulation of the serotonin reuptake system, clinical trials in healthy humans have demonstrated that BM possesses a significant effect on the retention of newly-learned information. In several trials utilizing a 300mg daily serving, BM was also shown to decrease the recall delay of newly learned information and reduce short term forgetfulness – suggesting that the herb’s effect on the serotonic and cholinergic systems are increasing the encoding (the literal storing) of memory information.
Beyond cognition and memory encoding, BM has also been demonstrated to function as a potent adaptogen and relaxant – which in the Core DAILY HEALTH PACK brain formula may help to smooth the effect curve of the product’s stimulants, reducing jitteriness or, “crash.”
Coffee Fruit Extract (Coffea arabica) (Fruit) (CognatiQ®)
CognatiQ®, an extract derived from the whole fruit Coffea arabica plant, is a clinically proven ingredient shown to stimulate the production of the neuroprotein, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). BDNF has been shown to be crucial in the development, maintenance and repair of neurons and also protect against neuro-degeneration. One study comparing other coffee, caffeine, and polyphenol compounds, showed that they were not statistically significant in increasing BDNF % compared to CognatiQ®. The unique polyphenol profile found in CognatiQ® showed to be superior in increasing BDNF concentration.
Huperzia serrata Extract (std. 1% Huperzine A)
Huperzia serrata is a compound found in the plant families of Huperziaceae, Lycopodiaceae, and Selaginella and is endemic to China. The Lycopodium alkaloid Huperzine-A, found in Core ZONE, was first isolated from a folk medicinal preparation in 1984.
This potent compound has been evaluated in numerous in vitro, in vivo, and human trials. These data suggest that Huperzine A’s mechanisms of action are most potent in the cortex, hippocampus, and striatum (at least in rats) – key regions in the brain responsible for forming, coordinating, and recalling memory. These effects are assisted by Huperzine A’s high oral bioavailability. Studies using microdialysis technique in rats, for example, showed that the response to Huperzine A was dose-dependent and substantially lowered the level of ACh in cortex.
Huperzine A has also shown promise in humans. Referred to as an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase, Huperzine A has shown positively impact cognition and memory. This is partly due to its inhibitory factors on acetylcholinesterase (an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine), which results in an increase in acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is known as a learning neurotransmitter so increased levels can be beneficial towards memory, and other neural improvements. In another study on memory and learning performance, 34 pairs of middle school students complaining of memory inadequacy were given a small dose of Huperzine A. The students were then match paired along several vectors and provided tests on working memory. The results of this study exhibited that HupA markedly improved the memory function of adolescent students.
JOINT
Turmeric Extract (95% curcuminoids) (Curcuma longa) (Root)
Turmeric is a root endemic to certain regions of Southeast Asia and India, and has been a staple in the Siddha traditional medicinal system for thousands of years. Turmeric is noted in Siddha texts for various uses, including as an ancient equivalent of an anti-microbial agent.
More recently, numerous studies seem to suggest that its primary bioactive constituent, curcumin, powerfully inhibits the enzymes that synthesize inflammatory compounds such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Basic research and molecular studies have now firmly established curcumin’s ability to dose-dependently and potently inhibit a transcription factor known as NF–kB – a molecule involved in the proliferation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, soft tissue destruction, and autoimmune responses.
Though Turmeric contains approximately 5% curcumin by weight, we have used a highly standardized extract of 95% - recognizing that the wealth of research on curcumin demands that it be included in clinical serving sizes.
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM)
MSM is a naturally occurring, organosulfur molecule that can be synthesized both naturally and synthetically from DSMO. While the majority of MSM present in the human body is ingested – either deliberately or accidentally – the compound does have a natural presence in certain tissues and fluids in the body, including cerebrospinal fluid. MSM appears to assist healthy biochemical communication between cells that may assist joint flexibility and mobility. While still emerging, certain data on MSM appears to show a promising role for the compound in the maintenance of proper joint function. Several studies demonstrate joint function increases on the WOMAC scale ranging from 20-35%, while animal data suggests equally significant results. Though not every trial on MSM reveals such significant results, a meta-analysis conducted in 2011 found that the overwhelming majority of clinical MSM trials featured function improvements over placebo.
BioPerine® Black Pepper Extract (Piper nigrum) (Fruit)
BioPerine® is a patented standardized extract from the fruit of Piper nigrum (black pepper). It’s studied benefits have continually shown improvements in bioavailability of nutrients it is surrounded by. When it comes to post exercise nutrition, efficiency and speed with which nutrients can enter the system and get to their target is of the upmost importance. The “window of opportunity” is much larger than what has been previously thought, but when your results weigh heavily on post-exercise nutrition, maximal absorption and use of nutrients is extremely important.
BioPerine® primarily works through mechanisms and channels that can inhibit intestinal motility and dilate blood vessels of the intestines (where absorption of nutrients occurs). This physiological action may cause increased absorption and digestion of nutrients.
Several studies looking at BioPerine®’s impact on oxidative stress have been performed. One study conducted on rats in 2013 looked at the influence of piperine on rats with developed disorders such as hypertension, increased inflammatory markers, and increased plasma liver enzymes after being fed a high carbohydrate and high fat diet. The results showed that after 16 weeks of supplementation with piperine these rats experienced normalized blood pressure, improved glucose tolerance, reduced markers of oxidative stress and inflammation, and improved liver function.
With more promising research being done on the effects of BioPerine® in the context of nutrient absorption, bioavailability, and its influence on certain health markers, it is only fitting that we include it in Core Life Line’s Liver support product.
HEART AND LIVER
Milk Thistle Extract (Silybum marianum) (Seed)
Silybum marianum, also known as milk thistle, is a medicinal thistle from the aster or daisy family that has been used in traditional medicines for many centuries for treatment of many different diseases. Many of these treatments have been to protect the liver and associated organs from damage/further damage. There is evidence to support that milk thistle, and specifically the silymarin compound that is found within it, exhibits a mechanism of action for hepatoprotection from free radicals through antioxidant activity, enhanced protein synthesis, and possible anti-inflammatory or immunomodulating effects. These free radicals are generated through the damage to cellular membranes called lipoperoxidation. Additionally, silymarin also enhances liver glutathione production through the inhibition of hepatocyte glutathione reduction. This can further contribute to the antioxidant support and defense for the liver. Several studies have shown improvements in liver function in individuals with certain liver diseases leading to these proposed benefits. In one in vitro human study, silymarin was shown to inhibit T-cell proliferation and proinflammatory cytokine secretion in a dose-dependent manner. Higher doses of silymarin were shown to specifically control hepatic inflammation responses in chronic liver diseases. It is important to note that in relation to liver diseases, milk thistle has been studied as a complimentary treatment method to traditional treatments and that it is important to live a healthy lifestyle to prevent these diseases as much as possible.
Hawthorn Berry Extract (Crataegus pinnatifida) (Fruit)
Hawthorne has been utilized for many centuries for its wide range of health benefits. One of these primary benefits is how it positively affects the cardiovascular system. The berries, or fruit, of the plant contain high amounts of bioflavonoids and proanthocyanins, substances shown to contain most of the health promoting qualities. These antioxidants have several mechanisms of action on the cardiovascular system. Hypotensive (lowering blood pressure) improvements can be seen through vasorelaxation through the stimulation of nitric oxide production. Several studies have investigated this benefit on blood pressure as well. One human study conducted on individuals with high blood pressure showed that the administration of 1200mg of Hawthorn Berry (slightly more than what we use in this product), noticed substantial improvements in blood pressure when compared to placebo.
Hawthorne Berry can also play a role in preventing atherosclerosis, or a buildup of plaque in the blood vessels that occurs due to an imbalance in blood fat levels (typically high triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol). If this plaque continues to accumulate, it can lead to blockages in the blood vessels carrying blood to vital organs, ultimately resulting to heart attack or stroke. Anti-atherosclerotic improvements can be seen through the downregulation of capsase-3 gene expression. The capsase-3 gene is known for being a proapoptotic (cell killing) gene that has been reported in heart failure and myocardial infarction (heart attack). The regulation of lipoprotein lipase (regulates the delivery of fats to body tissues) expression and raised excretion of bile acids can also benefit the arteries. Several animal studies have examined the positive impact of Hawthorne Berries on cholesterol. One study on mice showed that mice given the extract resulted in a lower total and LDL cholesterol, as well as between 30-45% lower liver triglyceride levels compared to mice that were not administered the extract.
On cardiac cells, these antioxidants downregulate capsase-3 gene expression and inhibit 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase, which can result in an increase in coronary flow, increase in relaxation velocity, and cause a positive inotropic effect (increase the strength of heart muscle contraction).
Coenzyme Q 10 (ubiquinone)
Coenzyme Q10, which is synthesized in the mitochondrial inner membrane, is an essential compound that plays many vital roles in the human body. Of these many roles, it is a key component in the electron transport chain in mitochondria necessary for ATP production. CoQ10 can also act as an intercellular antioxidant, protecting the plasmatic membrane against peroxidation. CoQ10 deficiency has been associated with less-than-optimal health status in organisms and has contributed to certain degenerative states involving blood sugar, the cardiovascular system, and musculoskeletal system. In relation to the cardiovascular system, oxidative stress is one of the main causes of cardiac decline. The antioxidant properties of CoQ10 are of particular importance in establishing normal function. It has been shown that individuals suffering from cardiac related abnormalities have significantly lower levels of CoQ10 as opposed to those with higher levels. With antioxidant effect and free radical neutralization being the primary mechanism of action, CoQ10 exhibits a secondary mechanism of action of well in playing a large role in the heart’s energetic needs. The process of cardiac contraction requires the release of Ca2+ from the SR and the following activation of the contractile proteins requires energy. It is believed that when there is myocardial failure, it is caused by a reduction in the production of energy from the mitochondria. This goes back to CoQ10s property of being a main component in the transport of electrons that are needed for ATP production. These two mechanisms of action have a particular importance for one’s quality of life as well as in maintaining proper cardiovascular function.
PROBIOTIC
Bromelain (Ananas comosus) (pineapple stem)
Bromelain is a collection of protein-digesting enzymes found in pineapple juice and in the stem of pineapple plants. It has been shown to have a myriad of health benefits including speed of recovery, antioxidant properties, and assisting cardiovascular and circulatory health. The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity is not very well understood, but like curcumin and Boswellia it appears to support inflammatory marker balance. Numerous studies have shown bromelain’s ability to assist and speed recovery time following various health related procedures.
Inulin
Inulin is a readily fermentable fiber by intestinal bacteria that can generate short chain fatty acids, which possess anti-inflammatory, immunoregulatory, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, and neuroprotective benefits. Inulin is especially beneficial when it comes to its effectiveness on the gut, such as reduced pH of the intestines, thus providing relief from GI distress and constipation which can lead to increased stool volume. Inulin has also shown effectiveness on reducing adipocyte size as well as improved glucose tolerance and an increase in energy expenditure.
Digestive Enzyme Blend (DigeSEB®)
One can easily make the argument that dietary enzymes – and, digestive enzymes – are the most consistently underrated and overlooked component to a supplementation regimen. These powerful little protein structures influence or outright control a vast, complex network of bodily functions. In a fitness-specific context, digestive enzymes play a crucial role in the breaking down of dietary carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into their constitutive parts, and therefore allow your body to use them in various processes (glycogenesis, protein synthesis, etc.).
Despite their critical function, many supplement companies overlook the necessity of digestive enzymes and do not include sufficient levels (and kinds) of enzymes in their products.
As usual, we take a much more comprehensive, clinical approach than the average. In Core Life Line’s Gut product, we have included a digestive enzyme blend comprised by:
- Proteases- breaks down proteins and other peptides
- Lactases- breaks down lactose
- Amylases- breaks down starches into useable sugars, such as glucose and maltose
- Lipases- breaks down fats/lipids which allow for a full and complete breakdown of all your daily dietary components.
Probiotic Blend (10 Billion CFU)
Under normal conditions, our gut microbiota – the constellation of intestinal flora that play innumerable physiological roles – are balanced between “good” and “bad” bacteria. The good bacteria confer immunity to us from pathogens, improve digestion of food, help regulate mood and more – while the “bad” bacteria cause a range of pathological conditions, invite pathogens, and generally wreak havoc on our bodies. The point of a well-designed probiotic is maintaining this intestinal balance in the “good” direction.
Using a probiotic supplement helps offset the microbiotic impact of stressors such as illness, medications (antibiotics), hormonal variations, and an incomplete diet. While the evidence is still emerging, the potential health benefits of probiotics have been seen in many conditions.
OMEGA 3
Nitrogen Barrier Production
Oil derived from marine animals – commonly referred to as “fish oils” – are widely consumed for the high amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids (such as DHA and EPA) that they contain and the potential health benefits that these fatty acids confer. Unfortunately, polyunsaturated fatty acids are notoriously unstable: they are composed of double-bonds between carbon atoms, a chemical structure that is notoriously susceptible to oxidation. (Oxidation is the process of producing oxygen species because of a compound’s exposure to oxygen.)
For fish oil, oxidation has a few deleterious effects – principally, the production of hydroperoxides (the first step in oxidation) and secondary oxygen products not only produce the rancid, “fish” smell typically associated with lower quality fish oil products; but perhaps more importantly, in breaking the double bond structure of the fish oil, these oxygen species degrade the integrity of the product and thus reduce their potential health benefits. The oxidation degradation is unfortunately widespread. One study found that 50% of 171 fish oil supplements in Canada exceeded the limits for at least one measure of oxidation, and 39% exceeded the international voluntary safety recommendations for total oxidation (TOTOX value).” Another study found that approximately 29% of fish oil supplements in the United States similarly exceeded recommended values.
Luckily, research has shown that reducing the exposure of fish oils to oxygen and environmental factors (humidity and temperature fluctuations) during the production process can significantly mitigate oxidation. One of the most effective ways to reduce oxygen exposure is to blanket the oil, as soon as its processed and produced, in an inert gas such as argon or nitrogen – thereby preventing the fish oil from encountering oxygen at all. While exact values will vary by product, research has shown that both primary oxidation (the production of hydroperoxides, measured in peroxide value, PV) and secondary oxidation (measured in TOTOX (total oxidation value) and a-nsidine values) are vastly reduced through a nitrogen blanket or barrier.
In sum, producing fish oils under a nitrogen blanket or barrier not only reduces the rancid smell typically associated with fish oil products; but vastly extends their shelf life and integrity.
Triglycerides vs Ethyl Ester Forms
We have established that how fish oils are produced may impact their viability as a dietary supplement. But the production process is not the only salient factor in fish oil efficacy and viability – the form that a fish oil takes is paramount, as well. Specifically, the differences between triglycerides and ethyl esters may be formative in how fish oils are absorbed and confer their potential health benefits.
First, a little primer on what triglycerides and ethyl esters are. Triglycerides are a molecular form common to almost all plant and animal species: a glycerol backbone with three fatty acids (in the case of fish oils, EPA, and DHA) attached to them. For example, the “stuff” of human adipose (fat) tissue is triglycerides. Ethyl Esters, on the other hand, lack a glycerol backbone – they are a single fatty acid molecule attached to an ethanol molecule. Unlike triglycerides, ethyl esters are not a natural molecular form and formed solely through chemical synthesis.
While the difference between triglycerides and ethyl esters as applied to fish oil may seem academic, it in fact has profound implications for the absorption and bioavailability of these oils. In very condensed form, the issue is twofold: how the fish oil is taken up into the bloodstream (absorption) and how it is made available to cells once that has occurred (bioavailability). In both contexts, there is evidence that triglycerides are superior to the ethyl ester form.
For bioavailability, the issue is how the small intestine breaks down each form of fish oil. As a natural product, our bodies are intrinsically capable of breaking down triglycerides via bile salts and pancreatic lipase. Once ingested, pancreatic lipase and bile salts are released, and in the small intestine, the triglyceride is broken down into so-called emulsion droplets – which can then easily be broken up, detaching the two fatty acid molecules from the glycerol backbone. Not so with ethyl esters. Not only is pancreatic lipase (by some estimates) 50% less effective in breaking down ethyl esters; but once digested, ethyl esters must be converted into triglycerides through the liberated fatty acids attaching to a glycerol molecule. Essentially, your body must reverse the entire metabolism of ethyl esters, then go through the normal triglyceride metabolism.
The biochemical differences between triglycerides and ethyl esters have been demonstrated in trials examining bioavailability and absorption efficiency. One study found that, when ingested in triglyceride form, EPA and DHA levels were 340% and 271%, respectively, as compared to the ethyl ester form. Additional research has found a 25% increase in plasma EPA and DHA levels over a six-month period; that ethyl esters are “poorly absorbed” by man; and that triglyceride form fish oils suffer less oxidation (on shelf) than the ethyl ester form.
EPA and DHA
Now that we know why producing fish oils under nitrogen barrier protects the integrity of fish oil, and why triglycerides are superior to ethyl esters, we have only one major question left: what benefits do fish oils (specifically, EPA and DHA) pose to humans?
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have myriad health benefits, but their best-studied (and approved by the FDA) use is to balance and maintain healthy triglyceride levels. Triglycerides, as we mentioned, are produced naturally by most animals. They are necessary for a wide range of physiological function, but their overabundance is implicated in several pathological conditions. Consequently, ingesting external forms of triglycerides – such as fish oils – can help balance triglycerides and maintain healthy levels. In perhaps the most robust meta-analysis to date, researchers examined 11 randomized human trials, comprised of 485 total individuals with a mean age of 25 to 49. The meta-analysis found robust evidence that DHA, specifically, exerts a significant triglyceride lowering and balancing effect. A similar meta-analysis focused on EPA found that its effects were comparable to DHA.
Both polyunsaturated fatty acids are best known for their triglyceride-lowering function, each exerts other interesting effects as well. Significant evidence suggests that EPA and DHA may mitigate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, molecules responsible for inducing the inflammation cascade in the body. Others studies suggest high levels of brain DHA are associated with verbal fluency and memory in healthy, normal adults – with one study finding that 6 months of DHA supplementation in young, healthy adults increased working memory assessed by recall.
One of fish oil’s (specifically, EPA’s) effects that may be of interest to fitness and physique athletes is its ability to induce AMPk (adenosine monophosphate kinase). AMPk, otherwise known as the “master metabolic switch,” is a heterotrimeric enzyme responsible for energy catabolism in muscle and fat cells. When activated, AMPk increases lipolytic (the catabolism of fat tissue) signaling as a means of energy provision. Several studies demonstrate that high levels of EPA indirectly stimulate AMPk activation via decreasing PPARy.
Though less well-studied or confirmed, emerging research suggests that DHA and EPA levels may be formative in maintaining healthy and normal moods, due to altering certain neurological proteins. These literatures require follow-up and replication, but show promise in establishing a new purpose for DHA and EPA supplementation.




